Implementing Tree Traversal Algorithms in Swift
Tree Structure is great for describing hierarchical data, but it depends on your application in regards to what kind of extra functionality it needs to have. We are going to discuss traversal algorithms, fundamental operations related to tree.
We have implemented a general-purpose Tree in previous Blog .
Traversal Algorithms
A traversal algorithm goes through all the nodes in a tree. We will be implementing two ways to traverse a tree:
Depth First Traversal
Depth First Traversal goes all the deep node in left and then to all other nodes. Starting from the top, it heads to the left in sequential order. If it can’t go left anymore, it’ll visit the current node and traverse to the right side.
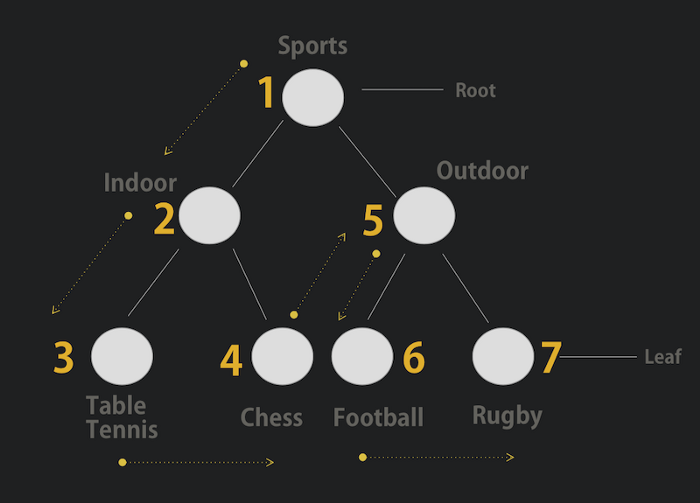
After implementing Depth First Traversal in our Sports example, the nodes it traverse, has to be in order of :
Sports -> Indoor -> Table Tennis -> Chess -> Outdoor -> Football -> Rugby
Let’s head over to the Swift implementation.
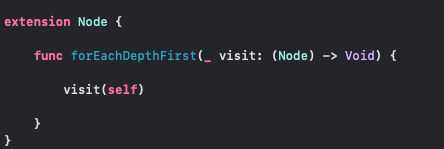
We will be adding an extension to Node Class, that we have implemented for Tree Structure.
In an extension of Node class, write a function with return type Void, since we are not returning anything, we will just print out the nodes in order of visiting.
First it visits the key node, which is the root node. Then, it visits children in order.
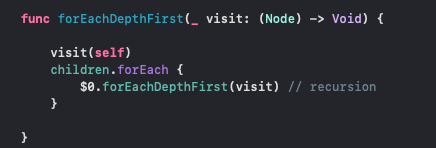
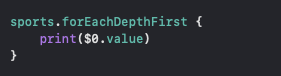
That’s it, we have implemented the Depth First Traversal. It is a simple algorithm, go ahead and print it out, to see the result.
Level Order Traversal
In Level Order Traversal, we go by the order of levels, in which nodes are laid out.
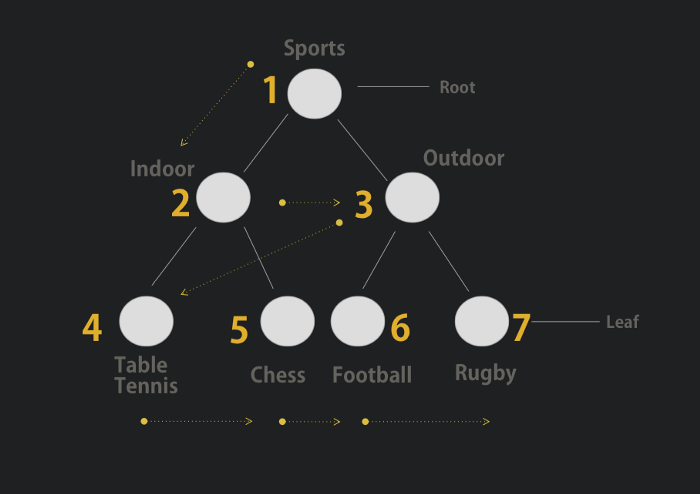
Considering the Sports example, it traverse the node in order of:
Sports -> Indoor -> Outdoor -> Table Tennis -> Chess -> Football -> Rugby
Implementation in Swift:
We have to implement a Queue to append and pop out the node in FIFO (First In First Out) Order. For more information about Queue, and its implementation, please refer to this blog.

After the implementation of queue. Under Node Extension, write a function with return type void. It is similar to function written for depth first traversal. First, it visits the key node, we’ll call the closure itself to print out the root node, then it visits the children.
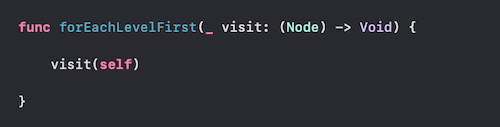
Next, for children, we have to create our queue, to keep track of all the nodes. We’ll need to add each node of the tree in queue, hence iterate through all the children.

Now, we are going to start dequeuing our elements. We will be using while loop, so that the queue can be dequeued to its last element. We have to dequeue each of the children.

Here we have implemented, Level First Traversal, now we will print out each of the element to verify the result.
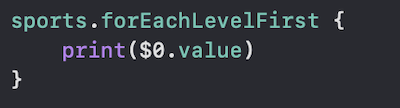
I hope it was helpful to you, here is all the above codes in one place, the complete Implementation of Tree Structure and Traversal Algorithms:
struct Queue<Element> {
var elements: [Element] = []
var isEmpty: Bool {
return elements.isEmpty
}
@discardableResult
mutating func enqueue(_ element: Element) -> Bool {
elements.append(element)
return true
}
mutating func dequeue() -> Element? {
return isEmpty ? nil : elements.removeFirst()
}
}
class Node<N> {
var value: N
var children:[Node] = []
init (value: N) {
self.value = value
}
func add(_ child: Node) {
self.children.append(child)
}
}
let sports = Node(value: "Sports")
let indoor = Node(value: "Indoor")
let outdoor = Node(value: "Outdoor")
sports.add(indoor)
sports.add(outdoor)
let tableTennis = Node(value: "Table Tennis")
let chess = Node(value: "Chess")
indoor.add(tableTennis)
indoor.add(chess)
let football = Node(value: "Football")
let rugby = Node(value: "Rugby")
outdoor.add(football)
outdoor.add(rugby)
print(sports)
extension Node {
func forEachDepthFirst(_ visit: (Node) -> Void) {
visit(self)
children.forEach {
$0.forEachDepthFirst(visit)
}
}
func forEachLevelFirst(_ visit: (Node) -> Void) {
visit(self)
var queue = Queue<Node>()
children.forEach {
queue.enqueue($0)
}
while let node = queue.dequeue() {
visit(node)
node.children.forEach {
queue.enqueue($0)
}
}
}
}
print("--- Depth First ---")
sports.forEachDepthFirst {
print($0.value)
}
print("--- Level First ---")
sports.forEachLevelFirst {
print($0.value)
}