Implementing Tree Data Structure in Swift
We are about to implement tree data structure in Swift. First, let’s understand basic about tree structure.
A tree is a data structure that simulates the hierarchical relationship between objects. The structure is just like natural tree with a root value and subtrees of children with a parent node.
Important Terms:
Root: The root of is the entry point to the tree data structure.
Node: Node is a block of data in the tree structure. Root itself is also a node.
Leaf: Leaf is a node with no children.
Level: Level of a node represents the generation of a node. Root is at level 0, while its next child is at level 1.
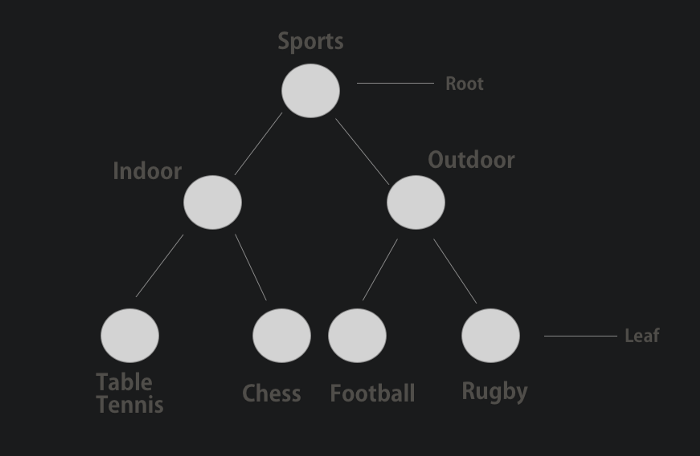
As shown in diagram, we have implemented a tree with real life example. Tree is made up of nodes, Indoor and Outdoor are children of root — Sports. Likewise, each of them has two children. Table tennis, chess, football and rugby, each of them is a leaf, as they don’t have children.
Implementing in Swift
We will be implementing the basic Sports tree structure in Swift. As trees are made up of nodes, we are going to create a basic node class in Swift Playground.

We have written a basic Node with a generic value “N” that it holds. It facilitates code reuse by allowing to build trees that hold different data types, just like arrays.
We’ve also declared an initializer which is required for initializing all non-optional stored properties for our class.
Additionally, we declared “children” as an array of nodes. Each child represents a node that is 1 level deeper that the current node.
Insertion
We want to add values to our tree, we need a function for it.

We have declared an add(child:) method in our Node class to handle insertion in our tree.
Let’s add values to create our Sports Tree.

We have created our tree which corresponds to the “Sports” tree structure.
We will implement Depth First Traversal and Level Order Traversal of Tree Structure in our next blog.
Complete code:
class Node<N> {
var value: N
var children:[Node] = []
init (value: N) {
self.value = value
}
func add(_ child: Node) {
self.children.append(child)
}
}
let sports = Node(value: "Sports")
let indoor = Node(value: "Indoor")
let outdoor = Node(value: "Outdoor")
sports.add(indoor)
sports.add(outdoor)
let tableTennis = Node(value: "Table Tennis")
let chess = Node(value: "Chess")
indoor.add(tableTennis)
indoor.add(chess)
let football = Node(value: "Football")
let rugby = Node(value: "Rugby")
outdoor.add(football)
outdoor.add(rugby)